PocketLab Voyager has an infrared rangefinder for measuring position and velocity. Learn the basics here.
Measuring Position and Velocity
Open the range finder in the app settings and display the rangefinder distance graph. Point the PocketLab Voyager at a desk or wall (Note: A white, solid surface will get the best signal). Move the PocketLab closer and then farther from the surface. The PocketLab is using an infrared signal to calculate its distance from the surface.

Measuring the Position of a Cart
Attach the PocketLab Voyager to the top of a cart so the IR rangefinder is pointing at a wall. Display the position graph and push the cart toward the wall to measure its movement.
Measuring Velocity
While you cannot graph velocity directly, you can automatically find the velocity of the Voyager using the slope of the position graph. Record a position graph, then open the data analysis tab in the bottom left. Zoom in on the section of the graph where you'd like to find the velocity by clicking and dragging on the graph. Double click to zoom out if needed. Then click curve fitting, and add a linear curve fit to see the slope of the line and the velocity of the sensor.

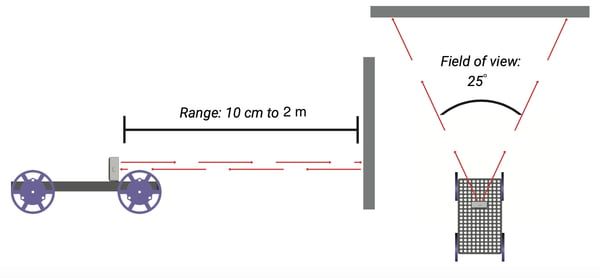
Range and field of view for IR rangefinder
As seen in the diagram above, the rangefinder has a range of up to 2 meters and a field of view of 25 degrees. The farther the target object is away from the PocketLab, the larger it needs to be to get the best signal as the field of view will get wider. The sensor may pick up objects off to the side of its field of view as it gets farther away.
Lessons that use the IR rangefinder
Browse PocketLab lessons on PocketLab Notebook (thepocketlab.com/notebook) to find more use cases and experiments using the IR rangefinder. You can also read more about how rangefinders work on this blog post.
