PocketLab Voyager, Weather, and Air can all measure air pressure. Learn about barometric pressure and how it is measured here.
What is barometric pressure?
Put your PocketLab in a bag, fill it with air, and seal the bag. When
you squeeze the bag, watch the pressure change.
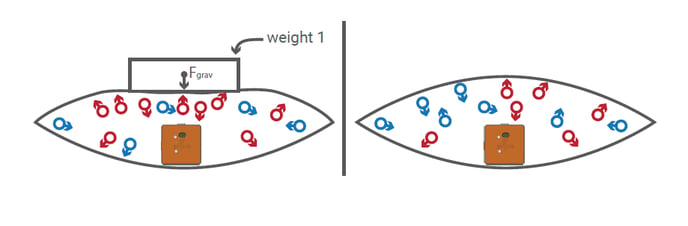
What is happening? When you squeeze the bag, the air molecules are being pushed closer and closer together and more are pushed back against the surface of the bag. You can feel the increase in pressure on your hand.
How does the sensor measure altitude?
There is more air pressure at lower altitudes due to gravity pulling the air molecules down. Your PocketLab can measure these small changes in air pressure and determine the change in altitude as well.
How does the sensor work?
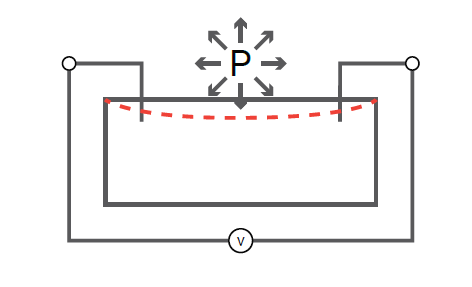
The sensor inside your PocketLab works on a similar principle. There is a sealed cavity that compresses and expands with the air around it, and a piezoresistor measures the tiny changes in the size of the cavity.
Measuring Altitude
Relative changes in altitude are calculated from changes in air pressure readings. Small fluctuations in air pressure can affect the altitude graph so the readings may move up and down slightly.
Since temperature can also affect air pressure, be aware of anything that might heat up the PocketLab like direct sunlight or if it has been charging recently. To get the most accurate altitude readings it is best to let the sensor adjust to ambient conditions for at least 2 minutes before starting a recording.
How to Zero Altitude
You can zero altitude by opening the Altitude settings menu and clicking Zero.

This calibration will last until you disconnect from the sensor. Calibration does not save since air pressure can vary significantly day to day. Best practice is to zero the graph right before you start a recording.
Note: At this time, memory mode recordings are unable to be calibrated.
